The harmful use of alcohol is one of the leading risk factors for health worldwide and has a direct implication on many health-related diseases, including those for mental and child health, , non-communicable diseases and mental health and injuries
Alcoholism has been defined by the World Health Organization as “a term of long-standing use and variable meaning, generally taken to refer to chronic continual drinking or periodic consumption of alcohol which is characterized by impaired control over drinking, frequent episodes of intoxication, and preoccupation with alcohol and the use of alcohol despite adverse consequences.
Alcohol use disorders continue to be an alarming health issue globally and it has been attributed to 2.5 million deaths per year worldwide. Although the consumption of moderate amounts of alcohol has been proven to have some beneficial effects, the risks associated with alcohol use especially in teenagers and adolescents definitely outweigh any benefit that may occur at a later point in life.
Pro-Health Foundation aims to reduce the health burden caused by the harmful use of alcohol and thereby to save lives, reduce disease and prevent injuries. This will be achieved through a counter advertisement that creates the needed awareness. The campaign aims at achieving a reduction in the intake of alcohol among the youth from the current rate of 41% to -20% by 2022.
ALCOHOL CONSUMPTION AND ITS HEALTH CONSEQUENCES
The consumption of high amounts of alcohol can predispose an individual to cardiovascular diseases, liver cirrhosis, cancer, trauma, diabetes, pancreatitis, gastrointestinal complications such as hemorrhagic gastritis, cerebrovascular diseases like stroke, and neurological complications such as alcoholic tremors, cerebellar degeneration, encephalopathy, impaired memory and mental disorders. The consumption of alcohol has been proven to adversely affect not only the systemic health but also the oral health of an individual. This review highlights the effects of alcohol consumption.
Cardiovascular diseases
Numerous epidemiological studies have observed a complex relationship between both the volume and patterns of alcohol consumption and the occurrence of cardiovascular diseases Specifically, volume and patterns of alcohol consumption have been shown to increase the risk of hypertensive heart disease. The relationship between alcohol and the onset of ischaemic heart disease or ischaemic strokes is complex; people who consume low-to-moderate amounts of alcohol and do not engage in irregular heavy drinking have a lower disease risk, while people who engage in irregular heavy drinking or who consume higher volumes of alcohol have a higher disease risk.
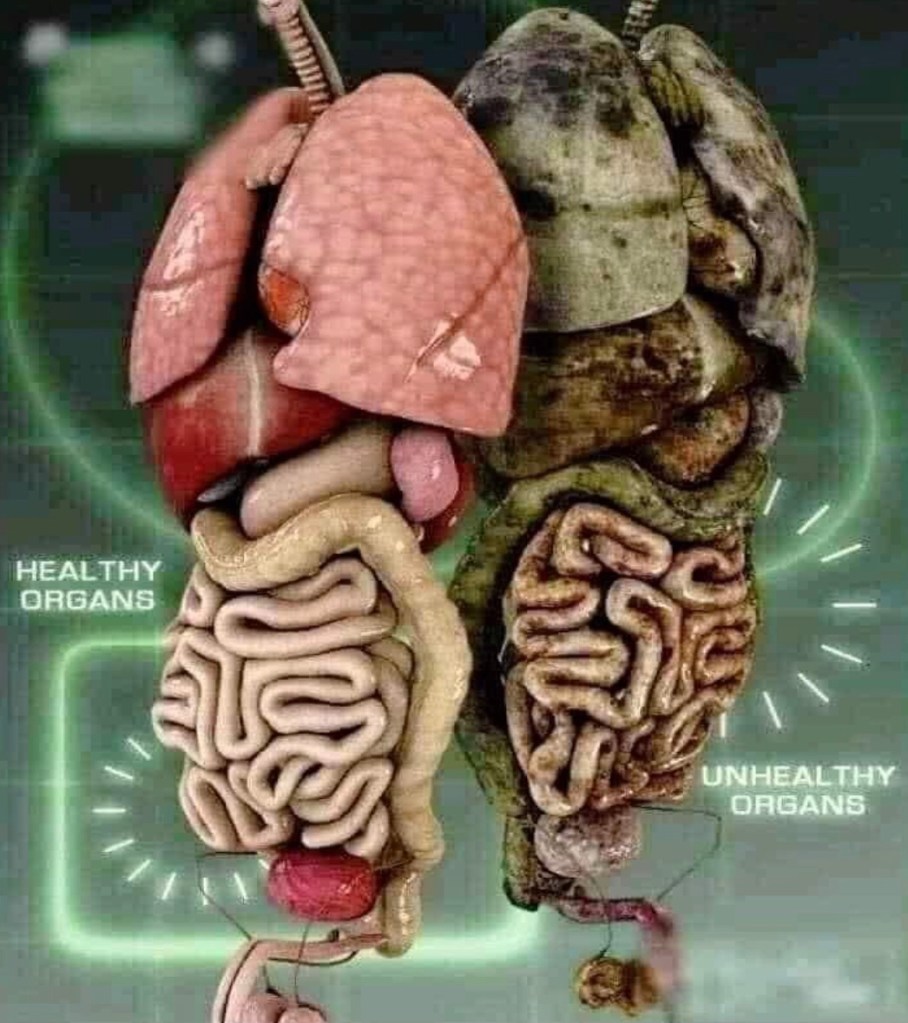
CANCERS
The biological mechanisms of alcohol-related carcinogenesis are not entirely understood, but several pathways have been identified by which alcohol is thought to contribute to cancer development. Most notably, alcohol has been shown to damage permanently the DNA strands in the cell and to inhibit DNA repair processes from functioning, particularly through acetaldehyde – the immediate product of alcohol metabolism. Alcohol use may also lead to nutritional deficiencies that affect DNA processing pathways.
LIVER DISEASES
The causal relationship of alcohol consumption and liver diseases is well established and alcohol has been shown to have an ability to cause hepatocellular damage through ethanol metabolism-associated mechanisms and malnutrition. Alcohol is one of the most frequent causes of liver diseases.
It is a well-established fact that chronic and excessive alcohol consumption adversely affects the health of the consumer.
HEALTH IS WEALTH!!!

BACS 21928
